pacman::p_load(sf, tidyverse)Hands-on Exercise 1.1: Geospatial Data Wrangling with R
Overview
In this hands-on exercise, I learn how to import and wrangling geospatial data in using appropriate R packages.
Getting Started
The code chunk below install and load sf and tidyverse packages into R environment.
Importing Geospatial Data
Importing polygon feature data
Dataset used:
Master Plan 2014 Subzone Boundary (Web) from data.gov.sg
Pre-Schools Location from data.gov.sg
Cycling Path from LTADataMall
Latest version of Singapore Airbnb listing data from Inside Airbnb
Click here to know more about st_read()
MP14_SUBZONE_WEB_PL, a polygon feature layer in ESRI shapefile format
mpsz = st_read(dsn = "data/geospatial", layer = "MP14_SUBZONE_WEB_PL")Reading layer `MP14_SUBZONE_WEB_PL' from data source
`C:\czx0727\ISSS624_\hands_on_ex1\data\geospatial' using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 323 features and 15 fields
Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 2667.538 ymin: 15748.72 xmax: 56396.44 ymax: 50256.33
Projected CRS: SVY21CyclingPath, a line feature layer in ESRI shapefile format
cyclingpath = st_read(dsn = "data/geospatial", layer = "CyclingPathGazette")Reading layer `CyclingPathGazette' from data source
`C:\czx0727\ISSS624_\hands_on_ex1\data\geospatial' using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 2558 features and 2 fields
Geometry type: MULTILINESTRING
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 11854.32 ymin: 28347.98 xmax: 42626.09 ymax: 48948.15
Projected CRS: SVY21PreSchool, a point feature layer in kml file format
preschool = st_read("data/geospatial/PreSchoolsLocation.kml")Reading layer `PRESCHOOLS_LOCATION' from data source
`C:\czx0727\ISSS624_\hands_on_ex1\data\geospatial\PreSchoolsLocation.kml'
using driver `KML'
Simple feature collection with 2290 features and 2 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XYZ
Bounding box: xmin: 103.6878 ymin: 1.247759 xmax: 103.9897 ymax: 1.462134
z_range: zmin: 0 zmax: 0
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Checking content of a simple dataframe
- Working with st_geometry()
st_geometry(mpsz)Geometry set for 323 features
Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 2667.538 ymin: 15748.72 xmax: 56396.44 ymax: 50256.33
Projected CRS: SVY21
First 5 geometries:MULTIPOLYGON (((31495.56 30140.01, 31980.96 296...MULTIPOLYGON (((29092.28 30021.89, 29119.64 300...MULTIPOLYGON (((29932.33 29879.12, 29947.32 298...MULTIPOLYGON (((27131.28 30059.73, 27088.33 297...MULTIPOLYGON (((26451.03 30396.46, 26440.47 303...- Working with glimpse()
glimpse(mpsz)Rows: 323
Columns: 16
$ OBJECTID <int> 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, …
$ SUBZONE_NO <int> 1, 1, 3, 8, 3, 7, 9, 2, 13, 7, 12, 6, 1, 5, 1, 1, 3, 2, 2, …
$ SUBZONE_N <chr> "MARINA SOUTH", "PEARL'S HILL", "BOAT QUAY", "HENDERSON HIL…
$ SUBZONE_C <chr> "MSSZ01", "OTSZ01", "SRSZ03", "BMSZ08", "BMSZ03", "BMSZ07",…
$ CA_IND <chr> "Y", "Y", "Y", "N", "N", "N", "N", "Y", "N", "N", "N", "N",…
$ PLN_AREA_N <chr> "MARINA SOUTH", "OUTRAM", "SINGAPORE RIVER", "BUKIT MERAH",…
$ PLN_AREA_C <chr> "MS", "OT", "SR", "BM", "BM", "BM", "BM", "SR", "QT", "QT",…
$ REGION_N <chr> "CENTRAL REGION", "CENTRAL REGION", "CENTRAL REGION", "CENT…
$ REGION_C <chr> "CR", "CR", "CR", "CR", "CR", "CR", "CR", "CR", "CR", "CR",…
$ INC_CRC <chr> "5ED7EB253F99252E", "8C7149B9EB32EEFC", "C35FEFF02B13E0E5",…
$ FMEL_UPD_D <date> 2014-12-05, 2014-12-05, 2014-12-05, 2014-12-05, 2014-12-05…
$ X_ADDR <dbl> 31595.84, 28679.06, 29654.96, 26782.83, 26201.96, 25358.82,…
$ Y_ADDR <dbl> 29220.19, 29782.05, 29974.66, 29933.77, 30005.70, 29991.38,…
$ SHAPE_Leng <dbl> 5267.381, 3506.107, 1740.926, 3313.625, 2825.594, 4428.913,…
$ SHAPE_Area <dbl> 1630379.27, 559816.25, 160807.50, 595428.89, 387429.44, 103…
$ geometry <MULTIPOLYGON [m]> MULTIPOLYGON (((31495.56 30..., MULTIPOLYGON (…- Working with head()
head(mpsz, n=5) Simple feature collection with 5 features and 15 fields
Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 25867.68 ymin: 28369.47 xmax: 32362.39 ymax: 30435.54
Projected CRS: SVY21
OBJECTID SUBZONE_NO SUBZONE_N SUBZONE_C CA_IND PLN_AREA_N
1 1 1 MARINA SOUTH MSSZ01 Y MARINA SOUTH
2 2 1 PEARL'S HILL OTSZ01 Y OUTRAM
3 3 3 BOAT QUAY SRSZ03 Y SINGAPORE RIVER
4 4 8 HENDERSON HILL BMSZ08 N BUKIT MERAH
5 5 3 REDHILL BMSZ03 N BUKIT MERAH
PLN_AREA_C REGION_N REGION_C INC_CRC FMEL_UPD_D X_ADDR
1 MS CENTRAL REGION CR 5ED7EB253F99252E 2014-12-05 31595.84
2 OT CENTRAL REGION CR 8C7149B9EB32EEFC 2014-12-05 28679.06
3 SR CENTRAL REGION CR C35FEFF02B13E0E5 2014-12-05 29654.96
4 BM CENTRAL REGION CR 3775D82C5DDBEFBD 2014-12-05 26782.83
5 BM CENTRAL REGION CR 85D9ABEF0A40678F 2014-12-05 26201.96
Y_ADDR SHAPE_Leng SHAPE_Area geometry
1 29220.19 5267.381 1630379.3 MULTIPOLYGON (((31495.56 30...
2 29782.05 3506.107 559816.2 MULTIPOLYGON (((29092.28 30...
3 29974.66 1740.926 160807.5 MULTIPOLYGON (((29932.33 29...
4 29933.77 3313.625 595428.9 MULTIPOLYGON (((27131.28 30...
5 30005.70 2825.594 387429.4 MULTIPOLYGON (((26451.03 30...Plotting Geospatial Data
- Using plot - Default plot of an object is a multi-plot of all attributes, up to a reasonable maximum as shown below
plot(mpsz)Warning: plotting the first 9 out of 15 attributes; use max.plot = 15 to plot
all
- Choose only the geometry
plot(st_geometry(mpsz))
- Plot sf using special attributes
plot(mpsz["PLN_AREA_N"])
Assigning EPSG code to a simple feature data frame
This is an example the coordinate system of mpsz simple feature data frame by using st_crs() of sf package as shown in the code chunk below.
st_crs(mpsz)Coordinate Reference System:
User input: SVY21
wkt:
PROJCRS["SVY21",
BASEGEOGCRS["SVY21[WGS84]",
DATUM["World Geodetic System 1984",
ELLIPSOID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
ID["EPSG",6326]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,
ANGLEUNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]]],
CONVERSION["unnamed",
METHOD["Transverse Mercator",
ID["EPSG",9807]],
PARAMETER["Latitude of natural origin",1.36666666666667,
ANGLEUNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8801]],
PARAMETER["Longitude of natural origin",103.833333333333,
ANGLEUNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8802]],
PARAMETER["Scale factor at natural origin",1,
SCALEUNIT["unity",1],
ID["EPSG",8805]],
PARAMETER["False easting",28001.642,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8806]],
PARAMETER["False northing",38744.572,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8807]]],
CS[Cartesian,2],
AXIS["(E)",east,
ORDER[1],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1,
ID["EPSG",9001]]],
AXIS["(N)",north,
ORDER[2],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1,
ID["EPSG",9001]]]]Wrong EPSG code because the correct EPSG code for svy21 should be 3414
mpsz3414 <- st_set_crs(mpsz, 3414)Warning: st_crs<- : replacing crs does not reproject data; use st_transform for
thatCheck the CSR again
st_crs(mpsz3414)Coordinate Reference System:
User input: EPSG:3414
wkt:
PROJCRS["SVY21 / Singapore TM",
BASEGEOGCRS["SVY21",
DATUM["SVY21",
ELLIPSOID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433]],
ID["EPSG",4757]],
CONVERSION["Singapore Transverse Mercator",
METHOD["Transverse Mercator",
ID["EPSG",9807]],
PARAMETER["Latitude of natural origin",1.36666666666667,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8801]],
PARAMETER["Longitude of natural origin",103.833333333333,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8802]],
PARAMETER["Scale factor at natural origin",1,
SCALEUNIT["unity",1],
ID["EPSG",8805]],
PARAMETER["False easting",28001.642,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8806]],
PARAMETER["False northing",38744.572,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8807]]],
CS[Cartesian,2],
AXIS["northing (N)",north,
ORDER[1],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
AXIS["easting (E)",east,
ORDER[2],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
USAGE[
SCOPE["Cadastre, engineering survey, topographic mapping."],
AREA["Singapore - onshore and offshore."],
BBOX[1.13,103.59,1.47,104.07]],
ID["EPSG",3414]]Transforming the projection of preschool from wgs84 to svy21
Let us perform the projection transformation by using the code chunk below.
- Print head of preschool
head(preschool, n=5)Simple feature collection with 5 features and 2 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XYZ
Bounding box: xmin: 103.8048 ymin: 1.299333 xmax: 103.8409 ymax: 1.435024
z_range: zmin: 0 zmax: 0
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
Name
1 kml_1
2 kml_2
3 kml_3
4 kml_4
5 kml_5
Description
1 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDREN'S COVE PRESCHOOL PTE.LTD.</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT9390</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>498CC9FE48CC94D4</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
2 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDREN'S COVE PTE. LTD.</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT8675</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>22877550804213FD</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
3 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDREN'S VINEYARD PRESCHOOL PTE. LTD</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT9308</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>B2FE90E44AD494E3</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
4 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDTIME CARE & DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PTE.LTD.</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT9122</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>1384CDC0D14B76A1</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
5 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILTERN HOUSE</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT2070</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>FB24EAA6E73B2723</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
geometry
1 POINT Z (103.8072 1.299333 0)
2 POINT Z (103.826 1.312839 0)
3 POINT Z (103.8409 1.348843 0)
4 POINT Z (103.8048 1.435024 0)
5 POINT Z (103.839 1.33315 0)- Transform the data
preschool3414 <- st_transform(preschool, crs = 3414)- Display data
head(preschool3414, n=5)Simple feature collection with 5 features and 2 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XYZ
Bounding box: xmin: 24821.92 ymin: 31299.16 xmax: 28844.56 ymax: 46303.16
z_range: zmin: 0 zmax: 0
Projected CRS: SVY21 / Singapore TM
Name
1 kml_1
2 kml_2
3 kml_3
4 kml_4
5 kml_5
Description
1 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDREN'S COVE PRESCHOOL PTE.LTD.</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT9390</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>498CC9FE48CC94D4</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
2 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDREN'S COVE PTE. LTD.</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT8675</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>22877550804213FD</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
3 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDREN'S VINEYARD PRESCHOOL PTE. LTD</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT9308</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>B2FE90E44AD494E3</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
4 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILDTIME CARE & DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PTE.LTD.</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT9122</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>1384CDC0D14B76A1</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
5 <center><table><tr><th colspan='2' align='center'><em>Attributes</em></th></tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>CENTRE_NAME</th> <td>CHILTERN HOUSE</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>CENTRE_CODE</th> <td>PT2070</td> </tr><tr bgcolor="#E3E3F3"> <th>INC_CRC</th> <td>FB24EAA6E73B2723</td> </tr><tr bgcolor=""> <th>FMEL_UPD_D</th> <td>20211201093631</td> </tr></table></center>
geometry
1 POINT Z (25089.46 31299.16 0)
2 POINT Z (27189.07 32792.54 0)
3 POINT Z (28844.56 36773.76 0)
4 POINT Z (24821.92 46303.16 0)
5 POINT Z (28637.82 35038.49 0)Importing the aspatial data
Import listing data
listings <- read_csv("data/aspatial/listings.csv")Rows: 3483 Columns: 18
── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Delimiter: ","
chr (6): name, host_name, neighbourhood_group, neighbourhood, room_type, l...
dbl (11): id, host_id, latitude, longitude, price, minimum_nights, number_o...
date (1): last_review
ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.Examine the dataset after importing to see if it is imported correctly
Creating a simple feature data frame from an aspatial data frame
The code chunk below converts listing data frame into a simple feature data frame by using st_as_sf() of sf packages
listings_sf <- st_as_sf(listings,
coords = c("longitude", "latitude"),
crs=4326) %>%
st_transform(crs = 3414)Examine the dataset below
glimpse(listings_sf)Rows: 3,483
Columns: 17
$ id <dbl> 71609, 71896, 71903, 275343, 275344, 28…
$ name <chr> "Villa in Singapore · ★4.44 · 2 bedroom…
$ host_id <dbl> 367042, 367042, 367042, 1439258, 143925…
$ host_name <chr> "Belinda", "Belinda", "Belinda", "Kay",…
$ neighbourhood_group <chr> "East Region", "East Region", "East Reg…
$ neighbourhood <chr> "Tampines", "Tampines", "Tampines", "Bu…
$ room_type <chr> "Private room", "Private room", "Privat…
$ price <dbl> 150, 80, 80, 55, 69, 220, 85, 75, 45, 7…
$ minimum_nights <dbl> 92, 92, 92, 60, 60, 92, 92, 60, 60, 92,…
$ number_of_reviews <dbl> 20, 24, 47, 22, 17, 12, 133, 18, 6, 81,…
$ last_review <date> 2020-01-17, 2019-10-13, 2020-01-09, 20…
$ reviews_per_month <dbl> 0.14, 0.16, 0.31, 0.17, 0.12, 0.09, 0.9…
$ calculated_host_listings_count <dbl> 5, 5, 5, 52, 52, 5, 7, 52, 52, 7, 7, 1,…
$ availability_365 <dbl> 89, 89, 89, 275, 274, 89, 365, 365, 365…
$ number_of_reviews_ltm <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, …
$ license <chr> NA, NA, NA, "S0399", "S0399", NA, NA, "…
$ geometry <POINT [m]> POINT (41972.5 36390.05), POINT (…Geoprocessing with sf package
sf package also offers a wide range of geoprocessing (also known as GIS analysis) functions.
In this section below, I will demonstrate how to perform two commonly used geoprocessing functions, namely buffering and point in polygon count.
Buffering
Scenario: The authority is planning to upgrade the exiting cycling path. To do so, they need to acquire 5 metres of reserved land on the both sides of the current cycling path. I am tasked to determine the extend of the land need to be acquired and their total area.
Solution:
- Firstly, st_buffer() of sf package is used to compute the 5-meter buffers around cycling paths
buffer_cycling <- st_buffer(cyclingpath,dist=5, nQuadSegs = 30)- This is followed by calculating the area of the buffers as shown in the code chunk below.
buffer_cycling$AREA <- st_area(buffer_cycling)- Lastly, sum() of Base R will be used to derive the total land involved
sum(buffer_cycling$AREA)1774367 [m^2]Point-in-polygon count
Scenario: A pre-school service group want to find out the numbers of pre-schools in each Planning Subzone.
Solution:
- The code chunk below performs two operations at one go. Firstly, identify pre-schools located inside each Planning Subzone by using st_intersects(). Next, length() of Base R is used to calculate numbers of pre-schools that fall inside each planning subzone.
mpsz3414$`PreSch Count`<- lengths(st_intersects(mpsz3414, preschool3414))- Check the summary statistics of the newly derived PreSch Count field by using summary() as shown in the code chunk below.
summary(mpsz3414$`PreSch Count`) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
0.00 0.00 4.00 7.09 10.00 72.00 - To list the planning subzone with the most number of pre-school, the top_n() of dplyr package is used as shown in the code chunk below.
top_n(mpsz3414, 1, `PreSch Count`)Simple feature collection with 1 feature and 16 fields
Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 39655.33 ymin: 35966 xmax: 42940.57 ymax: 38622.37
Projected CRS: SVY21 / Singapore TM
OBJECTID SUBZONE_NO SUBZONE_N SUBZONE_C CA_IND PLN_AREA_N PLN_AREA_C
1 189 2 TAMPINES EAST TMSZ02 N TAMPINES TM
REGION_N REGION_C INC_CRC FMEL_UPD_D X_ADDR Y_ADDR SHAPE_Leng
1 EAST REGION ER 21658EAAF84F4D8D 2014-12-05 41122.55 37392.39 10180.62
SHAPE_Area geometry PreSch Count
1 4339824 MULTIPOLYGON (((42196.76 38... 72**DIY: Calculate the density of pre-school by planning subzone.
- Firstly, the code chunk below uses st_area() of sf package to derive the area of each planning subzone.
mpsz3414$Area <- mpsz3414 %>% st_area()mpsz3414 <- mpsz3414 %>% mutate(`PreSch Density` = `PreSch Count`/Area * 1000000)Explorotary Data Analysis (EDA)
Firstly, we will plot a histogram to reveal the distribution of PreSch Density. Conventionally, hist() of R Graphics will be used as shown in the code chunk below.
hist(mpsz3414$`PreSch Density`)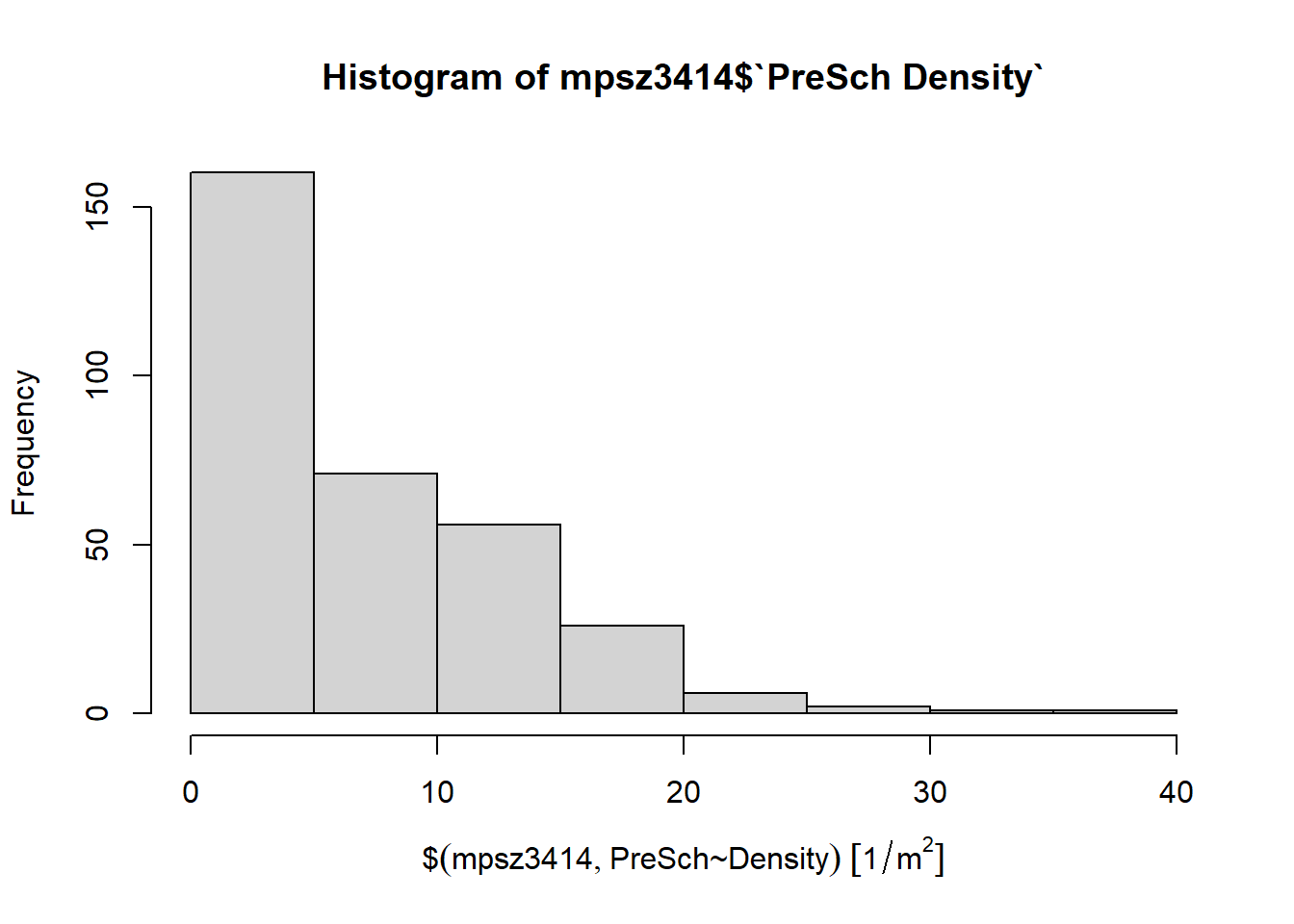
In the code chunk below, appropriate ggplot2 functions will be used.
ggplot(data=mpsz3414,
aes(x= as.numeric(`PreSch Density`)))+
geom_histogram(bins=20,
color="black",
fill="light blue") +
labs(title = "Are pre-school even distributed in Singapore?",
subtitle= "There are many planning sub-zones with a single pre-school, on the other hand, \nthere are two planning sub-zones with at least 20 pre-schools",
x = "Pre-school density (per km sq)",
y = "Frequency")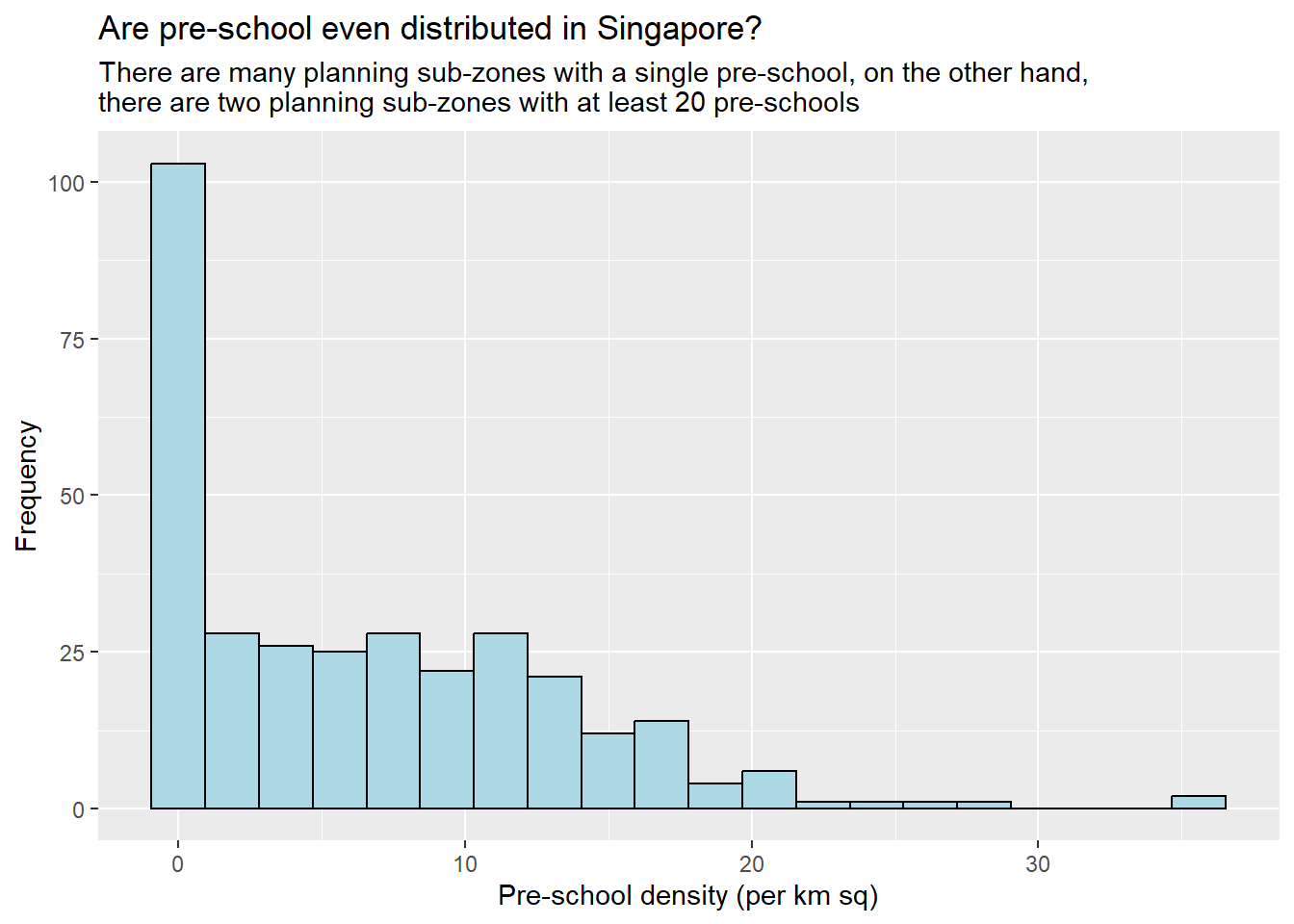
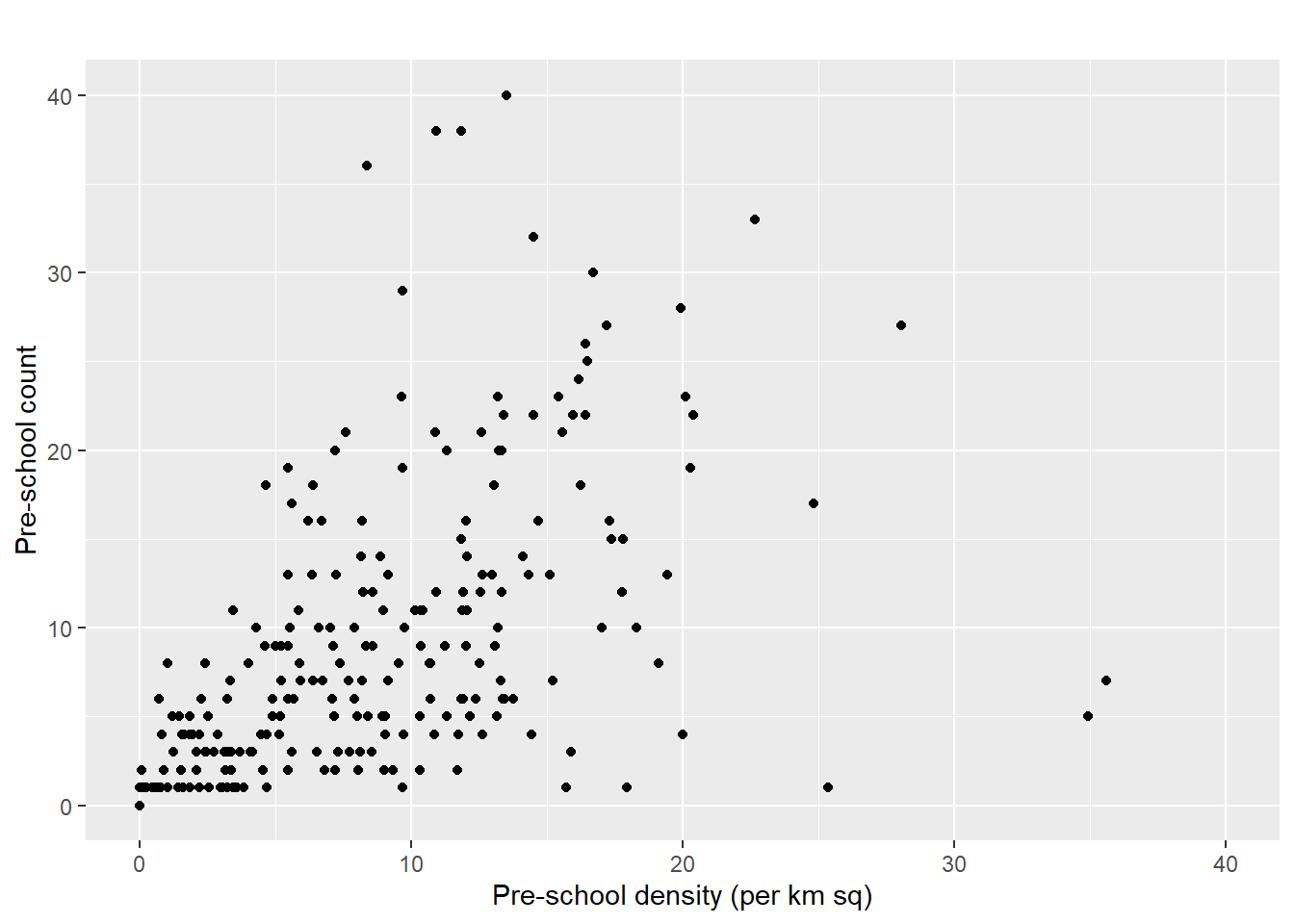
** Using ggplot2 method, plot a scatterplot showing the relationship between Pre-school Density and Pre-school Count.
ggplot(data=mpsz3414,
aes(y = `PreSch Count`,
x= as.numeric(`PreSch Density`)))+
geom_point(color="black",
fill="light blue") +
xlim(0, 40) +
ylim(0, 40) +
labs(title = "",
x = "Pre-school density (per km sq)",
y = "Pre-school count")Warning: Removed 2 rows containing missing values (`geom_point()`).